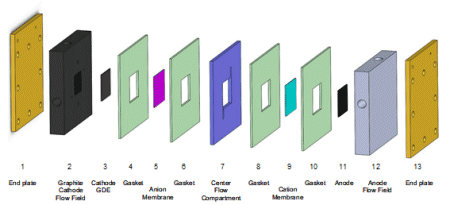
Dioxide Materials has Developed Electrochemical CO2 to Formate/Formic Acid 3 Compartment Cell Design with Record Performance
GDE Cathode with Nanoparticle Tin Electrocatalyst and Sustainion® Ionomer
Sustainion® Anion Exchange Membrane
Center Compartment with Strong Acid Media
Anode Side Cation Membrane
Anode with IrO2 Electrocatalyst
Extended Formic Acid Cell Operating Performance with Dioxide Materials’ Sustainion® Membranes
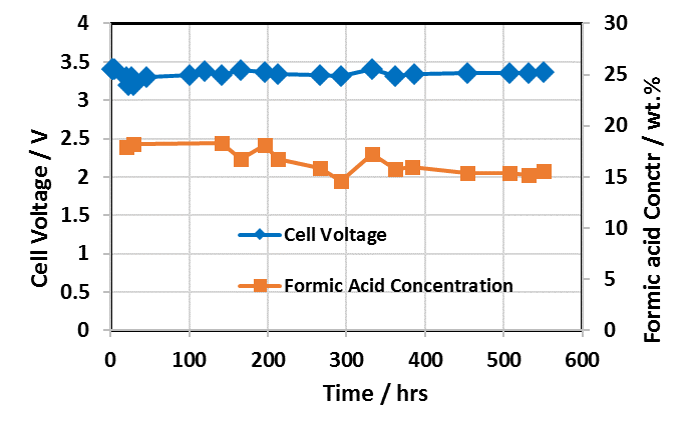
Cell Run 550 Hours – IrO2 on Carbon Anode
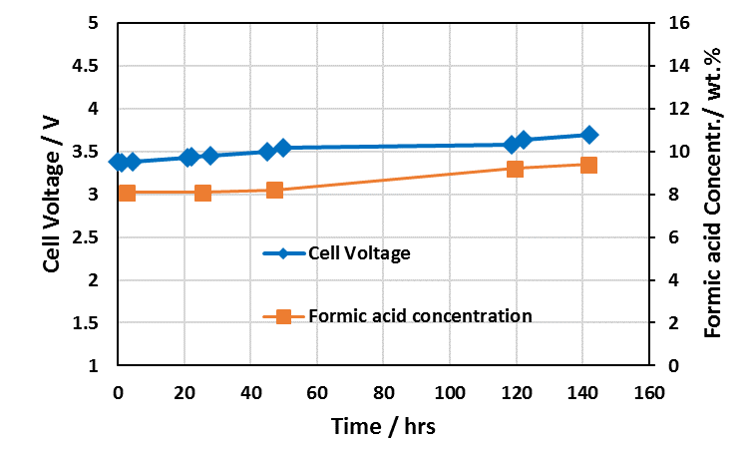
Cell Run 140 Hours – IrO2 on Ti Anode
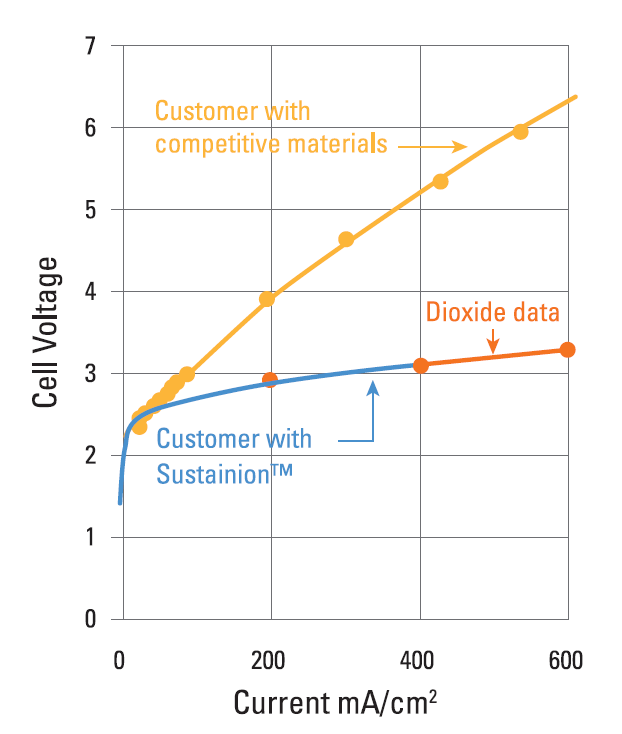
Examples of the Performance Seen With Dioxide Materials’ CO2 to Formic Acid Electrolyzer
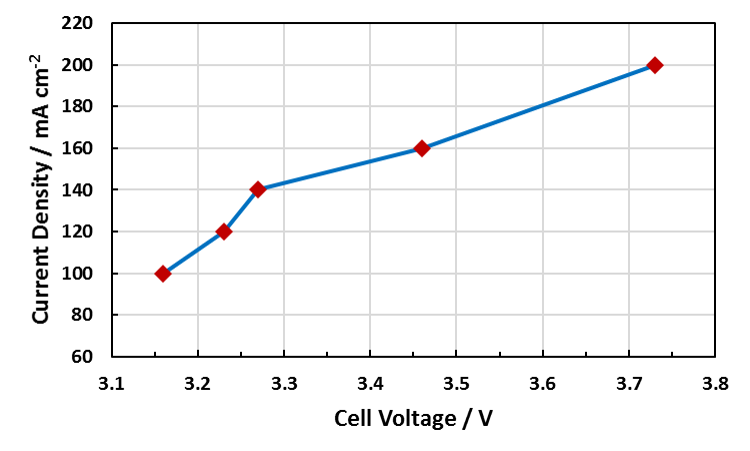
Cell Voltage vs. Current Density
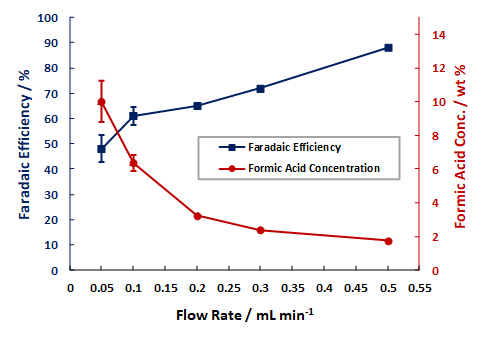
Formic Acid FE and Wt% vs. Single Pass Flow Rate
Dioxide Materials’ Patented Catalysts Make the Process Economic
Electrochemical Reduction of CO2 to Formic Acid
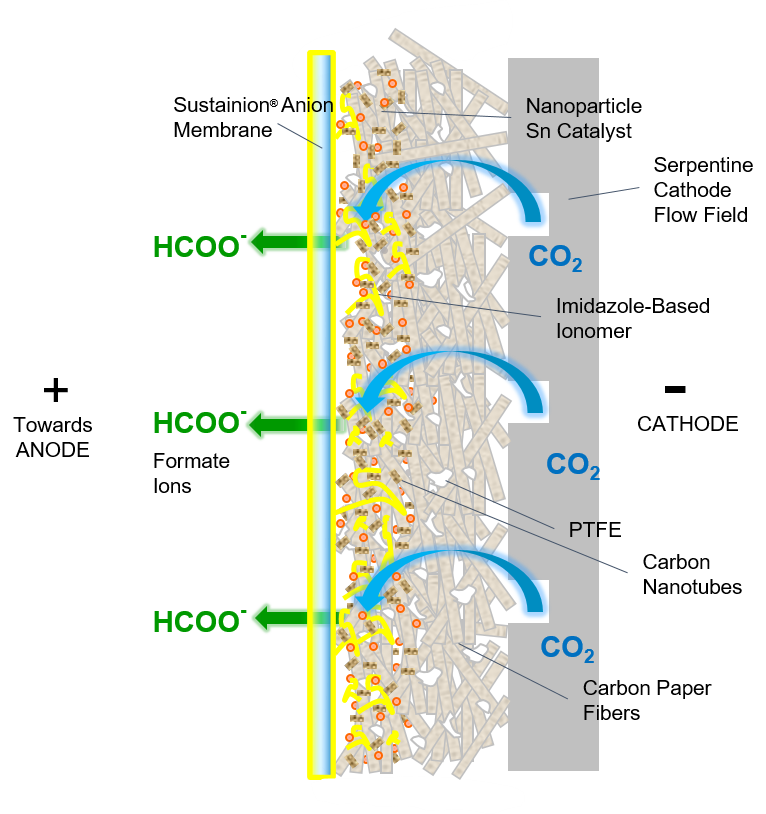
Cathode Catalyst Components
GDE Cathode
Tin nanoparticle electrocatalyst, carbon nanotubes, and imidazole-based ionomer
Sustainion® Anion Membrane
Why such good performance?
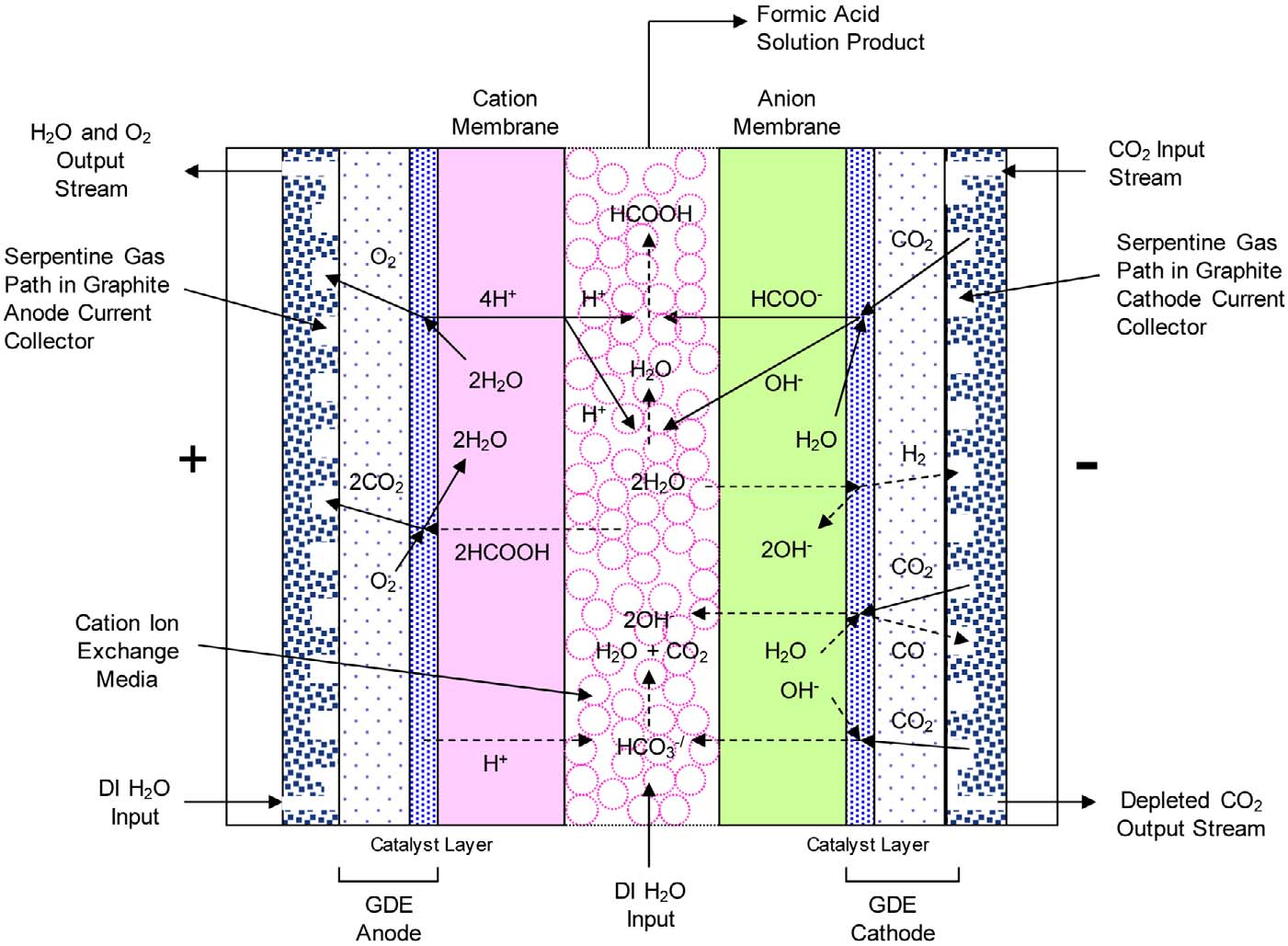
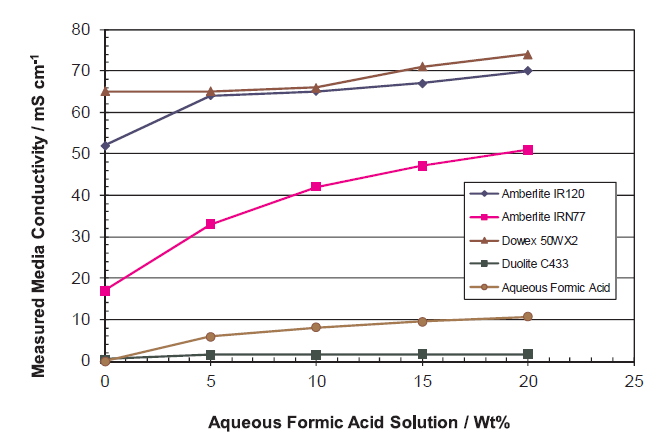
Center Compartment Ion Conductivity
Dioxide Materials’ Advantages
Better Materials
| Membrane | ASR in 1 M KOH, 60 °C | pH Range |
| Sustanion® 37-50 | 0.045 Ω-cm2 | 2-14 |
| Fumasep FAS-50 | 0.37 Ω-cm2 | 0-13 |
| Nafion 115 | 0.52 Ω-cm2 | 0-13 |
| Fumasep FAPQ-375 | 0.83 Ω-cm2 | 0-11 |
| AMI-7001 | 2.0 Ω-cm2 | 0-10 |
| PBI | 8.3 Ω-cm2 | 2-10 |
| Neosepta ACN | >50 Ω-cm2 | 0-8 |
Better Performance