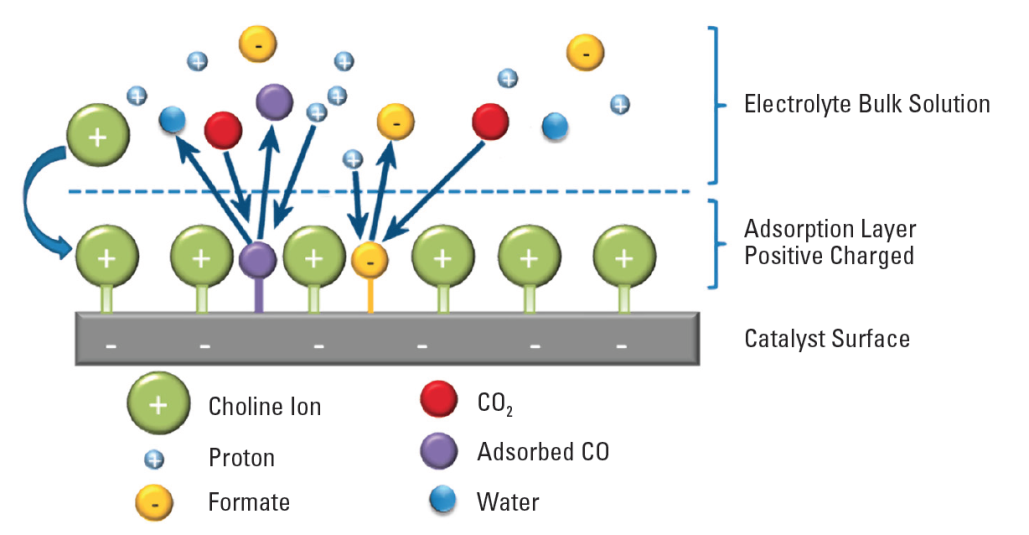
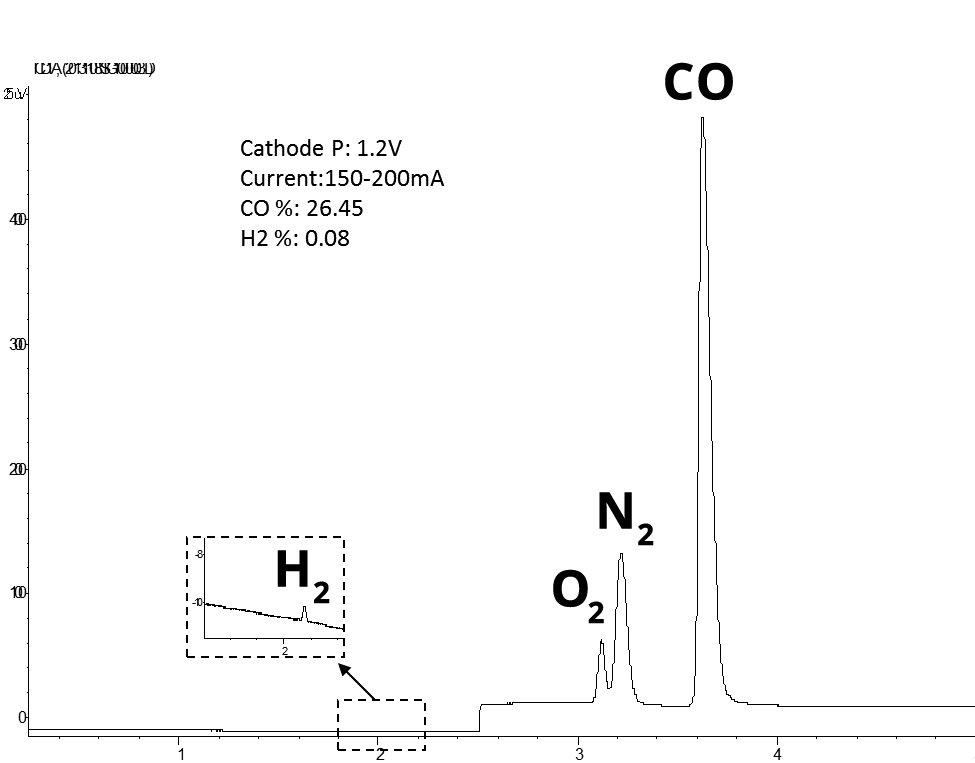
CO2 Recycling: Conversion Of Waste CO2 Into Valuable Fuels And Chemicals
The reduction of greenhouse gas emissions is becoming a pressing concern for many industries. However, most current technologies treat CO2 as a liability that must be removed at very high cost. Dioxide Materials offers an electrochemical route for the conversion of CO2, a waste feedstock, to CO or formic acid, thereby creating value from waste and reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
If we are successful, we can change the world by promoting energy security and independence. Our vision is to recycle CO2 back to fuels, using renewable energy as an input thereby providing a route to renewable fuels and chemicals that does not compete with the food supply.
Advantages of Dioxide Materials’ Technology
Reduced CO2 emissions
Reduced use of fossil fuels
Path to renewable fuels and chemicals
Potential to consume billions of tons of CO2
Dioxide Materials’ Process
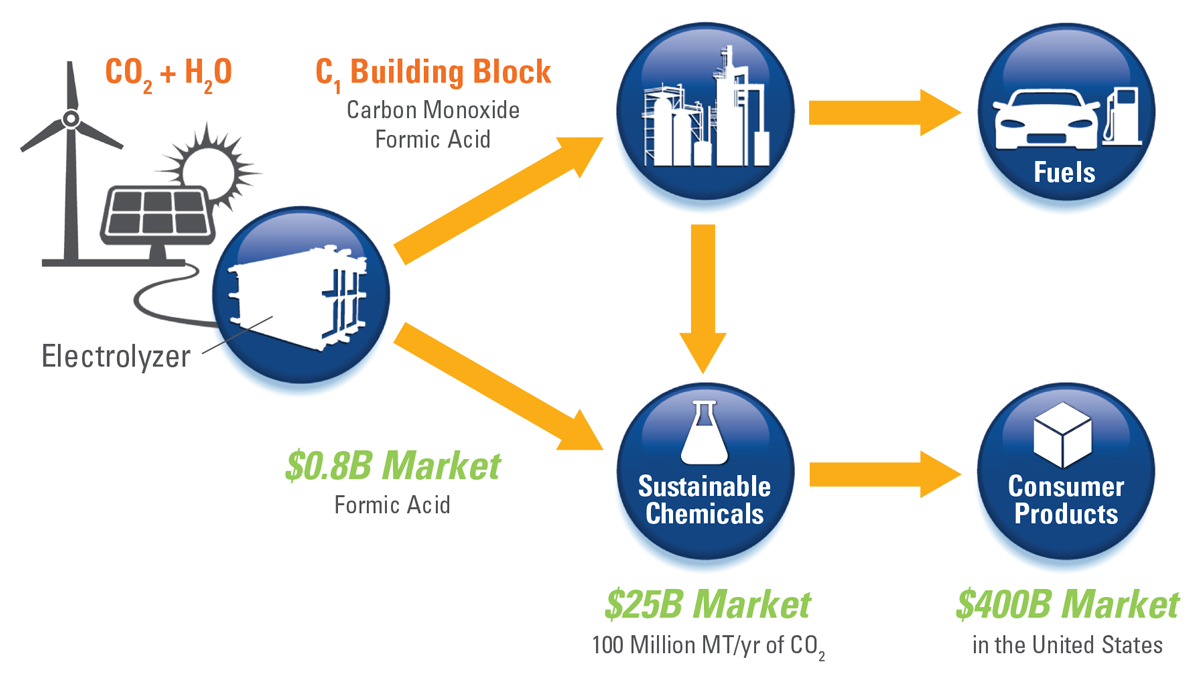
Dioxide Materials‘ process uses an electrolyzer to convert CO2 into C1 building blocks. Subsequent chemical processes convert the C1 building blocks into high value fuels and chemicals. Dioxide Materials’ patented catalysts lower the cost of converting carbon dioxide into C1 building blocks by a factor of 3. Dioxide materials also has patent pending processes to convert the C1 building blocks into high value chemicals , creating the first cost-competitive route to large volume, renewable fuels and chemicals.
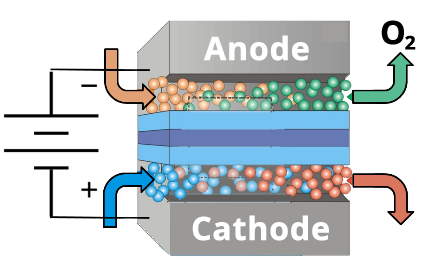
- How does it work? CO2 converted to CO + O2 in an electrolyzer.
- What is novel about it? Use combination of metallic and organic catalysts to lower the overpotential by 0.8 V.
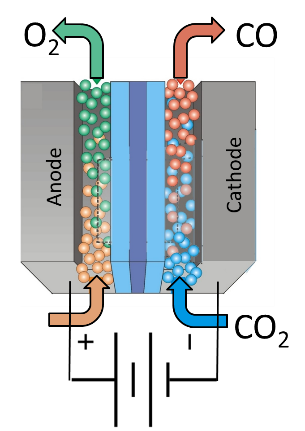
CO2 Electrolyzers Are Used Convert CO2 Into C1 Building Blocks
CO Formation On Silver
H2O ? 2H+ + 2 e?+ ½ O2
CO2 + 2H+ + 2 e? ? CO + H2O
HCOOH Formation On Tin
H2O ? 2H+ + 2 e?+ ½ O2

CO2 + 2H+ + 2 e? ? HCOOH
Another process is then used to convert the C1 intermediates to valuable products
Ethanol Production
Fuels Production
Dioxide Materials’ Advantages
Better Materials: Sustainion® Membranes
| Membrane | ASR in 1 M KOH, 60 °C | pH Range |
| Sustanion® 37-50 | 0.045 Ω-cm2 | 2-14 |
| Fumasep FAS-50 | 0.37 Ω-cm2 | 0-13 |
| Nafion 115 | 0.52 Ω-cm2 | 0-13 |
| Fumasep FAPQ-375 | 0.83 Ω-cm2 | 0-11 |
| AMI-7001 | 2.0 Ω-cm2 | 0-10 |
| PBI | 8.3 Ω-cm2 | 2-10 |
| Neosepta ACN | >50 Ω-cm2 | 0-8 |
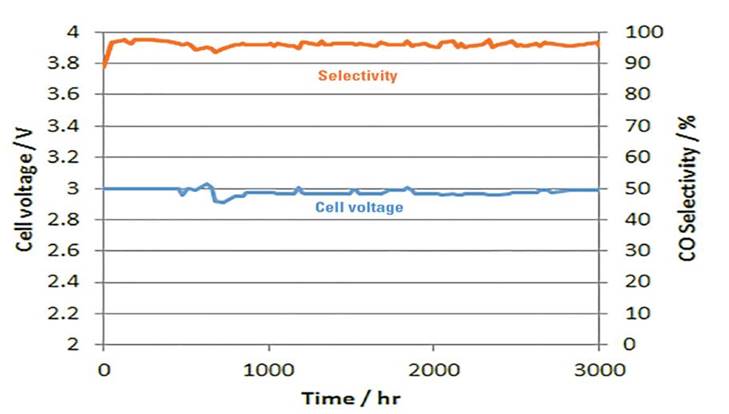
Better Performance
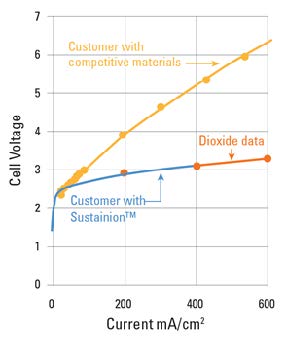
Examples of the Performance Seen With Dioxide Materials’ CO2 electrolyzer
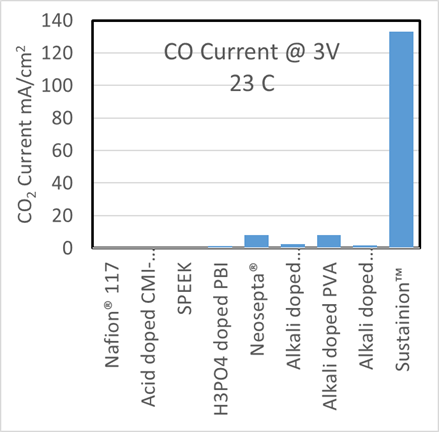
The voltage needed to maintain 200 mA/cm2 at room temperature.

Dioxide Materials’ Sustainion® membranes enable electrolyzers to outperform the competition
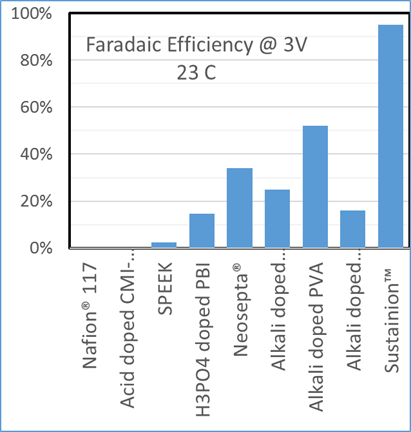
Dioxide Materials’ patented catalysts make the process economic
Co-catalyst Lowers the Overpotential
Challenge for electrochemical reduction of CO2
- High overpotential due to the formation of intermediate species
- Low selectivity due to the side reactions
Breakthrough
-
- Combined ionic liquid with Ag metal
- Lowered the overpotential to 0.17V
- Suppressed side reactions
- Improved the selectivity to 98%
Rosen, et al., Science 334, 643 (2011)
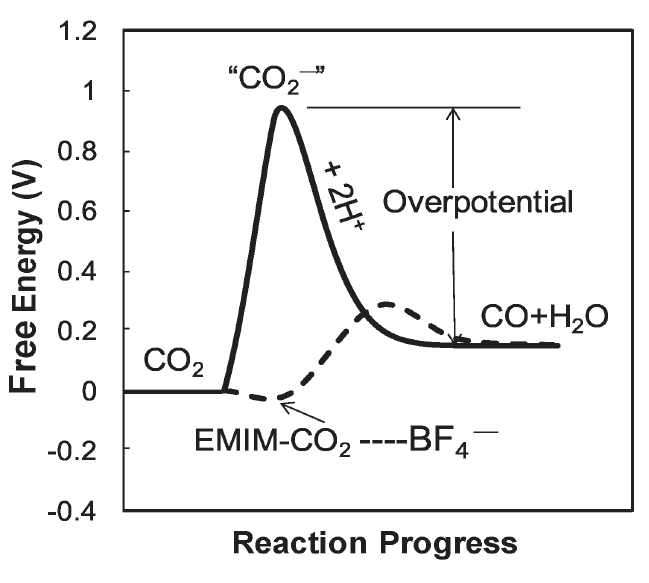
Why such good performance?
EMIM creates low barrier pathway
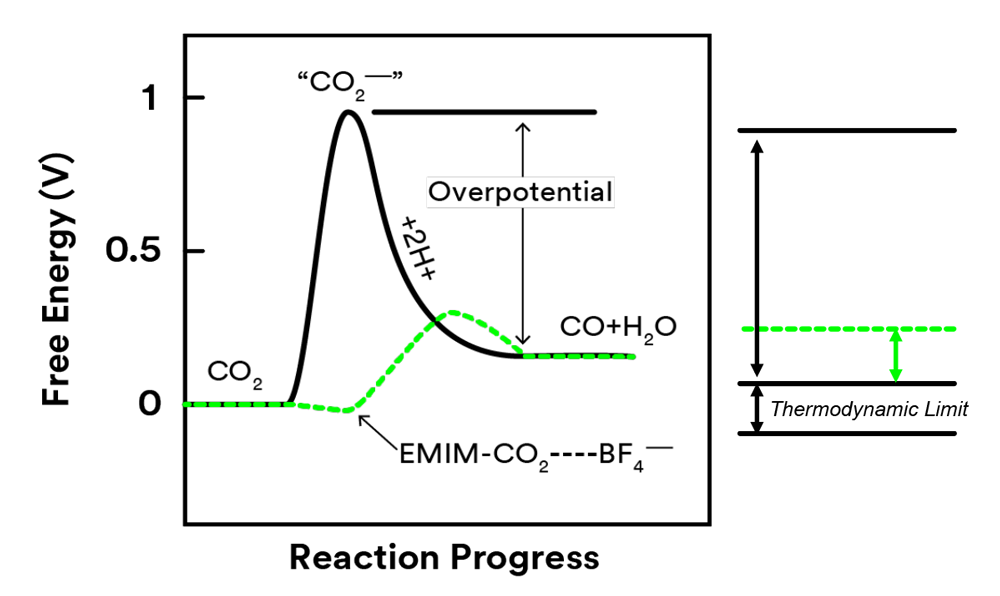

EMIM blocks side reactions